 Over the past two years, nations around the world attempted to cut down the usage of coal in order to slow air pollution.
Over the past two years, nations around the world attempted to cut down the usage of coal in order to slow air pollution.
Several policies were passed, and the construction of many coal plants was halted. China, in particular, halted plans for over a hundred coal plants, putting it at the forefront of the fight against climate change. The country produces half of all global energy generated from coal.
But, due to economic reasons, China recently pulled out of its coal policies, and many energy companies are resuming the construction of coal plants.
Surprisingly, the main reason for this sudden change is that energy companies are not able to produce as much power as before. As China needs the power badly, the decision has been made to let the coal energy plants run again.
Coal as Fossil Fuel
Coal is a non-renewable source of energy and the biggest source of electricity in the world.
Humans have been mining and using coal as a heat source for thousands of years. Coal was especially used during the Industrial Revolution and today as an inexpensive source of energy to produce heat, electricity, steel, and more.
Unfortunately, coal takes millions of years to form, and there is a limited amount available. In addition, the mining of coal ruins the landscape and pollutes the surrounding water and air. The burning of coal also produces toxins and releases sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, impacting the air quality as well as producing acid rain and smog.
Finally, coal consumption releases pollutants and greenhouse gases into the air, specifically carbon dioxide. These gases trap heat and increase the temperature of the atmosphere. As these greenhouses do not easily disappear, the impact has been quite evident - over the past twenty years, the burning of fossil fuels had made up three-fourths of man-made emissions. And the result is global warming - our Earth is heating up.
Coal Usage Around The World
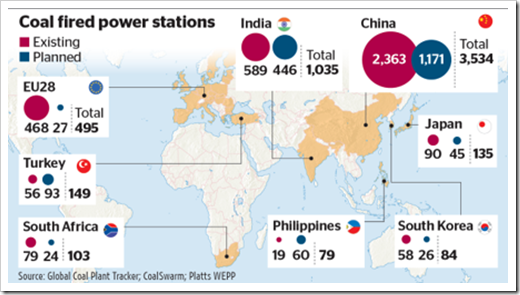 However, China is not the only country that is bringing back coal plants. The United States, another top producer of coal, may have stopped the coal plants domestically, but coal exports still continue to fuel the power plants and steel mills in other nations.
However, China is not the only country that is bringing back coal plants. The United States, another top producer of coal, may have stopped the coal plants domestically, but coal exports still continue to fuel the power plants and steel mills in other nations.
In addition, the construction of new coal plants continues to take place worldwide, under the supervision of big energy companies. See this map for global coal plants.
To address global warming, we need to take urgent action and replace coal with renewable sources of energy like wind and solar.
Sources: NYTimes, National Geographic, Chinadialogue, Foreignpolicy, BBC








