 Can you imagine living in a world where cars are powered spontaneously as they speed past roads, and entire households are fueled by their walls?
Can you imagine living in a world where cars are powered spontaneously as they speed past roads, and entire households are fueled by their walls?
Well, this crazy dream has just been brought a little closer to life!
Researchers at MIT and Harvard have created a battery from cement, carbon black (a kind of fine charcoal), and water. Known as a supercapacitor, this could be a huge turning point in the future of energy storage.
Let's find out more.
How Do These Supercapacitors Work?
Typical batteries you may have seen around your home depend on a chemical reaction to generate electrical energy. Capacitors, on the other hand, rely on the separation of charges (positive and negative) between two conductive plates immersed in an electrolyte solution. Supercapacitors are very large capacitors, capable of holding a lot of charge.
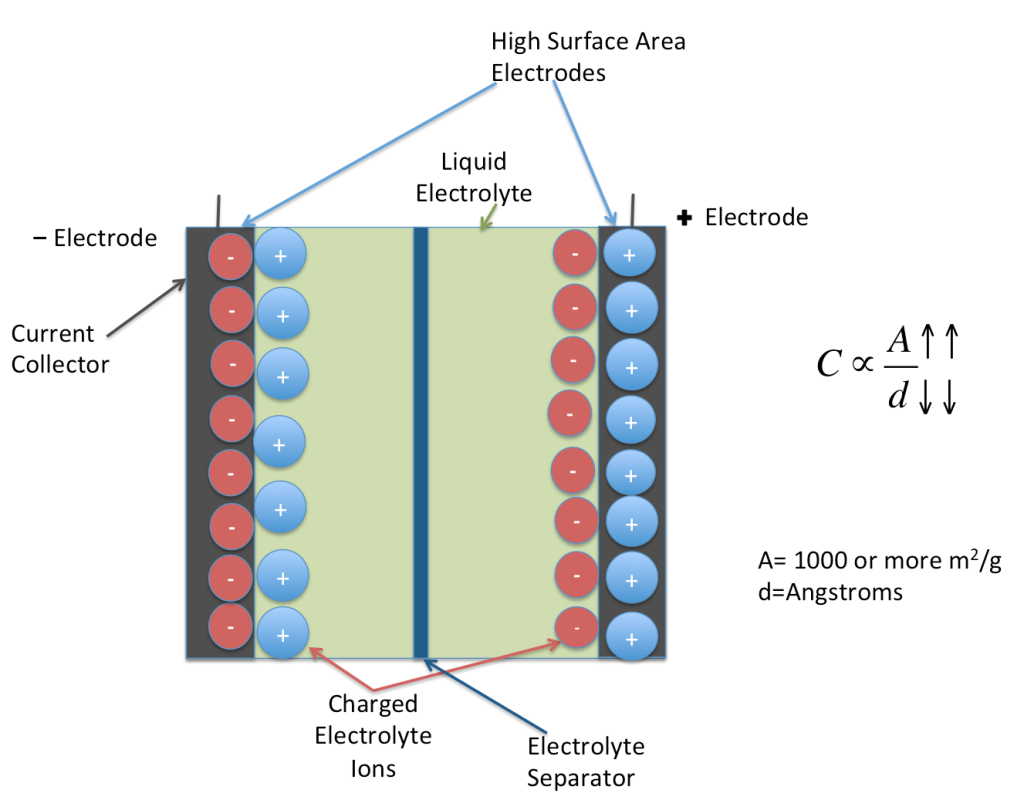 How did scientists create this new supercapacitor battery? They first prepared a mixture consisting mainly of cement, carbon black, along with water and let it harden over time. Once hardened, discs are cut out of the hardened mixture, soaked in potassium chloride (a salt), and separated with a membrane.
How did scientists create this new supercapacitor battery? They first prepared a mixture consisting mainly of cement, carbon black, along with water and let it harden over time. Once hardened, discs are cut out of the hardened mixture, soaked in potassium chloride (a salt), and separated with a membrane.
When a voltage is applied to this setup, potassium chloride breaks down into negative and positively charged particles. Both types of charged particles are attracted to the disc of the opposite charge. With the membrane in between, a separation of charges is created -- and you have an electric field!
You might ask if the mixture is so simple, what makes these batteries so special? The trick is actually in the materials used -- carbon black and cement. The amount of power held by a supercapacitor depends on the surface area of the plates. At a microscopic level, the combination of cement and carbon black creates many pores during hardening which increases the surface area, thus attracting more electrons and storing larger amounts of electricity!
Why Are These Batteries Important?
Previously, scientists have used lithium-based batteries to store renewable energy (eg. sun, wind). Renewable energy is a better alternative to fossil fuels (eg. oil, coal), which are more expensive, require more energy, and have a negative impact on the environment.
 Since the sun and wind’s energy are irregular, lithium-based batteries are used to store their energy when needed. However, lithium is scarce, as there are only 101 lithium mines in the world. Along with its low supply, lithium mining also causes greenhouse emissions.
Since the sun and wind’s energy are irregular, lithium-based batteries are used to store their energy when needed. However, lithium is scarce, as there are only 101 lithium mines in the world. Along with its low supply, lithium mining also causes greenhouse emissions.
On the other hand, these supercapacitors have the advantage of using accessible and cheap materials. While cement production is responsible for 5-8% of global carbon dioxide emissions, it is the most widely used material in construction. The initial applications may be in isolated buildings that are not connected to the grid.
However, these cement batteries are not completely ready yet. Currently, researchers are working on creating the most desirable mixture of carbon black, cement, and water depending on whether certain applications require stronger or weaker cement, along with other factors.
Meanwhile, we can eagerly await further developments, in the hope that one day we can drastically reduce our dependence on fossil fuels!
Sources: BBC, MIT, ASME, IFLScience







