 A decade ago, only 120,000 EV cars were sold worldwide in a year. Did you know that now that many are sold each week?
A decade ago, only 120,000 EV cars were sold worldwide in a year. Did you know that now that many are sold each week?
This growing need for batteries to power these cars is leading to a huge surge in building battery plants across the globe. And it seems that this hype will only continue to increase in the future!
But do you know exactly what these battery plants are? And why is there so much demand for them in the first place?
Battery Parts and Plants at a Glance
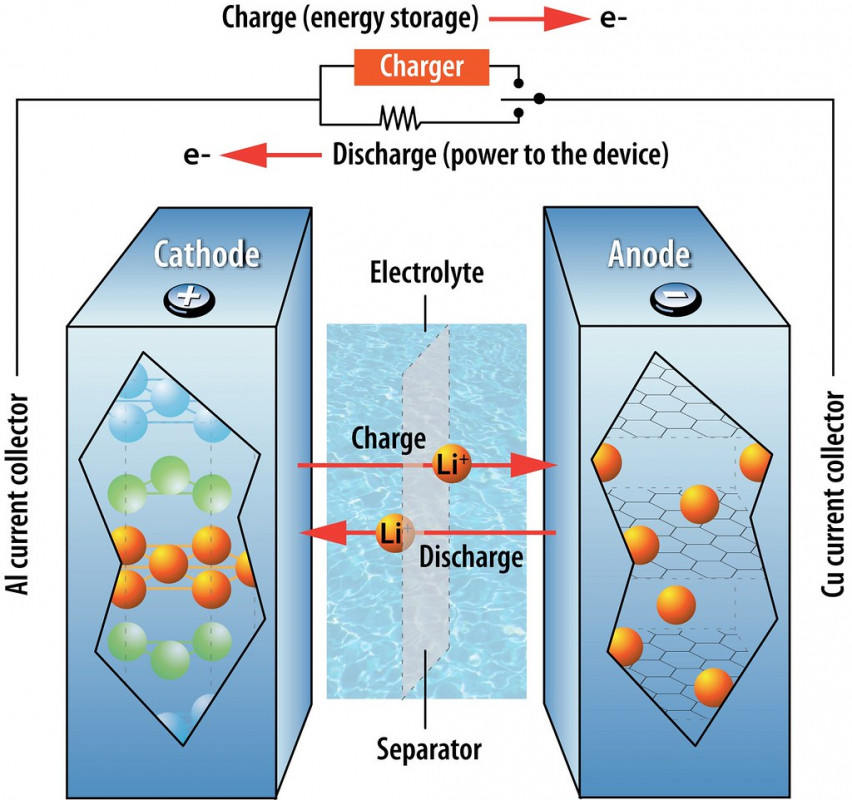 The basic structure of an electric, or EV battery, is a cell. Many cells combined are called a module, and many modules combined are called a pack. The pack is what is installed in a vehicle.
The basic structure of an electric, or EV battery, is a cell. Many cells combined are called a module, and many modules combined are called a pack. The pack is what is installed in a vehicle.
Inside the battery cell are many parts with different electrical charges such as --
- The Cathode - holds the positively charged particles
- The Anode - holds the negatively charged particles
- Separators - keep the cathode and anode from making contact
- Electrolyte - this substance carries particles from the cathode to mix with particles in the anode; causing a chemical reaction.
- Battery housing - a steel or aluminum casing that contains all the parts
Electric vehicle battery plants assemble components such as lithium-ion cells and terminal ends to produce these battery packs. However, the growing need for EV batteries is stressing the entire supply chain -- from the mining of minerals to dependence on China for batteries and the proper disposal of batteries without harmful environmental impacts.
How Batteries Work
 In a way, these car batteries work in a similar manner to our phone batteries. While the automobile is charging, the battery fills up. And when the car is running, this stored energy is used to power the engine motor that turns the tires and other car accessories such as air conditioning, heater, and headlights.
In a way, these car batteries work in a similar manner to our phone batteries. While the automobile is charging, the battery fills up. And when the car is running, this stored energy is used to power the engine motor that turns the tires and other car accessories such as air conditioning, heater, and headlights.
Electric batteries can last for ten to twenty years before they need replacement and this places an added demand on battery manufacturers. Fortunately, a vehicle’s auto batteries can be repurposed once they degrade and can be added to an energy storage system to power a house or building.
Already, manufacturers across the globe have planned or broken ground for the construction of dozens of battery plants. Major corporations such as Honda and LG Energy Solution have teamed up to build new battery plants in the United States.
The U.S federal plan for green energy requires that all newly-produced cars by 2035 be electric. In fact, by 2030, the global demand for electric batteries is predicted to be fifteen times greater than now! This reinforces how many more of these electric batteries will be needed in the future.
Sources: NY Times, EDF Energy, Batteries News, Visual Capitalist








