Planet Earth has hit a new milestone! On November 15, our planet began supporting a population of 8 billion humans.
Planet Earth has hit a new milestone! On November 15, our planet began supporting a population of 8 billion humans.
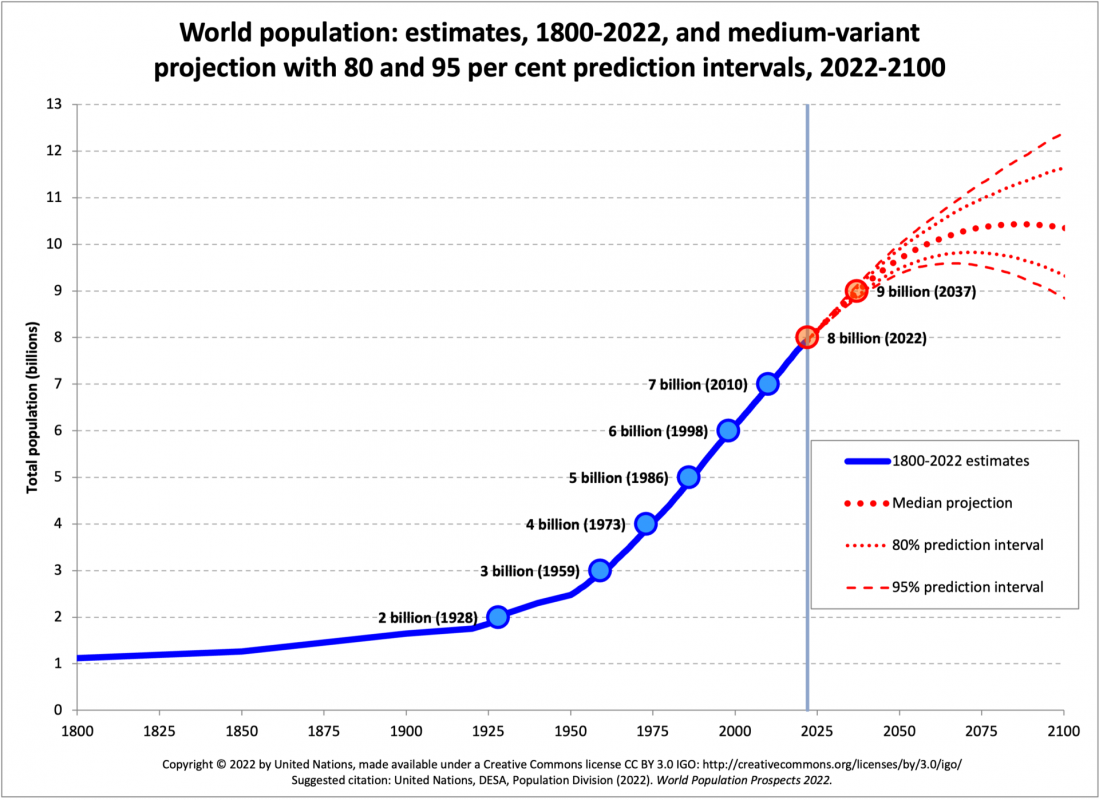
It has only been 11 years since we reached a milestone of 7 billion people. Every billionth person born is celebrated by the United Nations. For this milestone, a baby from the Dominican Republic was chosen to serve as the face of the children who helped us reach the 8 billion mark.
The rapid human population growth has been a result of advancements in human health and medicine, which contribute to longer lifespans. Most of the growth occurred in low-income countries in Asia and in sub-Saharan Africa.
The Hockey Stick Curve
For much of human history, our population stood at tens of millions. War, death, and disease kept the population in check, despite the agricultural revolution when humans settled down.
Two thousand years ago, the global population would have been the same as the current population of Nigeria or Brazil -- at about 200 million! The industrial revolution led to the first milestone of a billion in 1804. It would take another century before we hit the 2 billion mark in 1927.
Since then, we have had a meteoric rise, with the gap between the billions getting smaller and smaller. It has taken just 11 years from 7 billion to 8 billion! Most of this expansion has been in eight countries in Asia and Africa, according to the United Nations.
While our population has increased incredibly rapidly over the past century, officials expect future population growth to slow. We are projected to reach 9 billion people in 2037 and 10 billion in 2058. Experts hypothesize that the declining fertility rate in countries such as China and the expansion of reproductive education programs around the world will help plateau the population growth rate.
Question: How has the gap between the billions changed?
Impacts Of Population Growth
Population growth results in the necessity to produce and provide more resources for people, including education, public health, economic opportunity, water, food, and sanitation. These needs are even more pressing in low-income countries, where the fertility rate is highest. The growing demand for basic needs makes existing resources more valuable, which raises prices and increases public spending.
The increased consumption caused by population growth also leads to unsustainable practices and environmental challenges. One study shows that if everyone on Earth consumed as much as an average U.S. citizen does, we would need five Earths!
As our Earth supports more people, our ecosystems face more pressure from humans. This can amplify issues such as global warming, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity. These, in turn, could lead to disasters and pandemics as well as human migration and conflicts over dwindling resources.
While the growth in human population is a milestone to celebrate, it is a reminder that we need to take appropriate measures to protect our Earth so that it can protect the 8 billion of us!
Sources: NPR, NY Times, BBC, U.N, populationconnection.org